Cardinal Mobile SDK Android Integration Documentation V 2.2.4
Overview
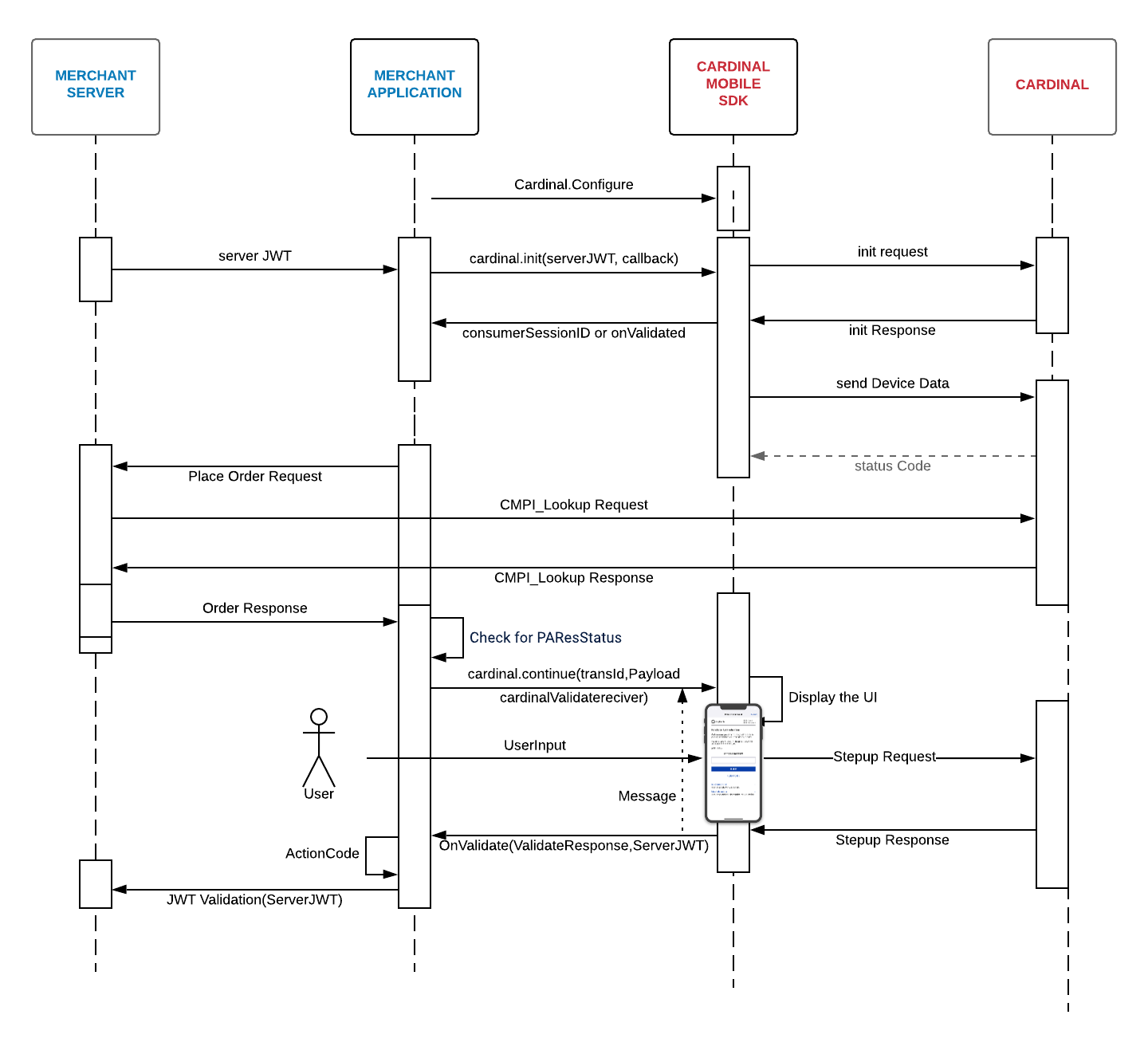
Activation Steps
Cardinal wants to get you up and running with CCA as quickly and seamlessly as possible. This section of the document will outline the simple steps that are necessary in order to take advantage of Cardinal Mobile SDK.
Step 1 - Update the Gradle Build Properties to Integrate Cardinal Mobile SDK
In Android Studio, open the app directory (which can also be labeled Module: app) and then open the build.gradle file. Double-check to make sure that you edit the Gradle file that is located in the app directory. Add the following contents to the Gradle file.
repositories {
...
maven {
url "https://cardinalcommerce.bintray.com/android"
credentials {
username ''//Bintray username
password ''//Bintray user API Key
}
}
}
dependencies {
...
//Cardinal Mobile SDK
implementation 'org.jfrog.cardinalcommerce.gradle:cardinalmobilesdk:2.2.4-1'
}
If your project uses Progurad, add the following lines into proguard-rules.pro file
-keep class com.cardinalcommerce.dependencies.internal.bouncycastle.** -keep class com.cardinalcommerce.dependencies.internal.nimbusds.**
For Bintray username and API Key please reach out to your client manager.
Step 2 - Configure Cardinal Mobile SDK
Upon successfully completing Integration in Step 1, get the instance of the cardinal object by Cardinal.getInstance(). SDK offers multiple configuration options for you (if not specified, everything is set to default). For more details: CardinalConfigurationOptions. Use the code snippet below for completing the cardinal.configure().
private Cardinal cardinal = Cardinal.getInstance();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
CardinalConfigurationParameters cardinalConfigurationParameters = new CardinalConfigurationParameters();
cardinalConfigurationParameters.setEnvironment(CardinalEnvironment.STAGING);
cardinalConfigurationParameters.setRequestTimeout(8000);
cardinalConfigurationParameters.setChallengeTimeout(5);
JSONArray rType = new JSONArray();
rType.put(CardinalRenderType.OTP);
rType.put(CardinalRenderType.SINGLE_SELECT);
rType.put(CardinalRenderType.MULTI_SELECT);
rType.put(CardinalRenderType.OOB);
rType.put(CardinalRenderType.HTML);
cardinalConfigurationParameters.setRenderType(rType);
cardinalConfigurationParameters.setUiType(CardinalUiType.BOTH);
UiCustomization yourUICustomizationObject = new UiCustomization();
cardinalConfigurationParameters.setUICustomization(yourUICustomizationObject);
cardinal.configure(this,cardinalConfigurationParameters);
}
private val cardinal: Cardinal = Cardinal.getInstance()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
val cardinalConfigurationParameters = CardinalConfigurationParameters()
cardinalConfigurationParameters.environment = CardinalEnvironment.STAGING
cardinalConfigurationParameters.requestTimeout = 8000
cardinalConfigurationParameters.challengeTimeout = 5
val rTYPE = JSONArray()
rTYPE.put(CardinalRenderType.OTP)
rTYPE.put(CardinalRenderType.SINGLE_SELECT)
rTYPE.put(CardinalRenderType.MULTI_SELECT)
rTYPE.put(CardinalRenderType.OOB)
rTYPE.put(CardinalRenderType.HTML)
cardinalConfigurationParameters.renderType = rTYPE
cardinalConfigurationParameters.uiType = CardinalUiType.BOTH
val yourUICustomizationObject = UiCustomization()
cardinalConfigurationParameters.uiCustomization = yourUICustomizationObject
cardinal.configure(this, cardinalConfigurationParameters)
}
Security Guide
After you configure cardinalSession, call method getWarnings to get the list of all the warnings for the particular device. Take further action based on the warnings found.
List of warnings can be accessed as follows:
List<Warning> warnings = cardinal.getWarnings();
Goto Security Guidance for detail.
Step 3 - Setup the Initial Call to Cardinal
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1600351095384&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=919&height=399) Calling
Calling Cardinal.init() will begin the communication process with Cardinal to ensure your user's experience is seamless, by authenticating your credentials (serverJwt) and completing the data collection process. By the time they are ready to checkout, all necessary pre-processing will be completed.Use the code snippet below for completing the cardinal.init().
cardinal = Cardinal.getInstance();
String serverJwt = "INSERT_YOUR_JWT_HERE";
cardinal.init(serverJwt ,
new CardinalInitService() {
/**
* You may have your Submit button disabled on page load. Once you are set up
* for CCA, you may then enable it. This will prevent users from submitting
* their order before CCA is ready.
*/
@Override
public void onSetupCompleted(String consumerSessionId) {
}
/**
* If there was an error with set up, Cardinal will call this function with
* validate response and empty serverJWT
* @param validateResponse
* @param serverJwt will be an empty
*/
@Override
public void onValidated(ValidateResponse validateResponse, String serverJwt) {
}
});
cardinal = Cardinal.getInstance()
val serverJwt = "INSERT_YOUR_JWT_HERE"
cardinal.init(serverJwt, object: CardinalInitService {
/**
* You may have your Submit button disabled on page load. Once you are set up
* for CCA, you may then enable it. This will prevent users from submitting
* their order before CCA is ready.
*/
override fun onSetupCompleted(consumerSessionId: String) {
}
/**
* If there was an error with setup, cardinal will call this function with
* validate response and empty serverJWT
* @param validateResponse
* @param serverJwt will be an empty
*/
override fun onValidated(validateResponse: ValidateResponse, serverJwt: String?) {
}
})
The following feature is deprecated as of 2.2.4
If you already have the credit card number and just need to pass it to Cardinal, you can pass it in Cardinal.init(). This makes it ideal in a flow where the consumer has already entered their payment information.
cardinal = Cardinal.getInstance();
String serverJwt = "INSERT_YOUR_JWT_HERE";
String accountNumber = "INSERT_YOUR_ACCOUNT_NUMBER" //minimum of 6 digits of the account number (credit Card number)
cardinal.init(serverJwt , accountNumber
new CardinalInitService() {
/**
* You may have your Submit button disabled on page load. Once you are setup
* for CCA, you may then enable it. This will prevent users from submitting
* their order before CCA is ready.
*/
@Override
public void onSetupCompleted(String consumerSessionId) {
}
/**
* If there was an error with setup, cardinal will call this function with
* validate response and empty serverJWT
* @param validateResponse
* @param serverJwt will be an empty
*/
@Override
public void onValidated(ValidateResponse validateResponse, String serverJwt) {
}
});
cardinal = Cardinal.getInstance()
val serverJwt = "INSERT_YOUR_JWT_HERE"
val accountNumber = "INSERT_YOUR_ACCOUNT_NUMBER" //minimum of 6 digits of the account number (credit Card number)
cardinal.init(serverJwt, accountNumber, object : CardinalInitService {
/**
* You may have your Submit button disabled on page load. Once you are setup
* for CCA, you may then enable it. This will prevent users from submitting
* their order before CCA is ready.
*/
override fun onSetupCompleted(consumerSessionId: String) {
}
/**
* If there was an error with setup, cardinal will call this function with
* validate response and empty serverJWT
* @param validateResponse
* @param serverJwt will be an empty
*/
override fun onValidated(validateResponse: ValidateResponse, serverJwt: String?) {
}
})
Step 4 - Create a Lookup Request/Response to Centinel
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1602880595948&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=750&height=361)
Create an API call to your backend server in order to send a Lookup Request (cmpi_lookup) to Cardinal's Centinel platform for initiating the Consumer Authentication transaction. The Centinel platform manages all of the routing and connectivity, as well as the rules engine for all of the various 3-D Secure protocols and versions. Please follow the Getting Started and Lookup Request/Response sections for completing your backend integration: Link
Required Field for identifying as an SDK transaction :
- <DeviceChannel>SDK</DeviceChannel>
- <DFReferenceId>ReferenceId</DFReferenceId>
ReferenceId is consumerSessionId returned on init completion, if no referenceID is passed in serverJwt. Else you can use that referenceID as DFReferenceId
Step 5 - Handle the Centinel Lookup Response and Create the Authentication Session
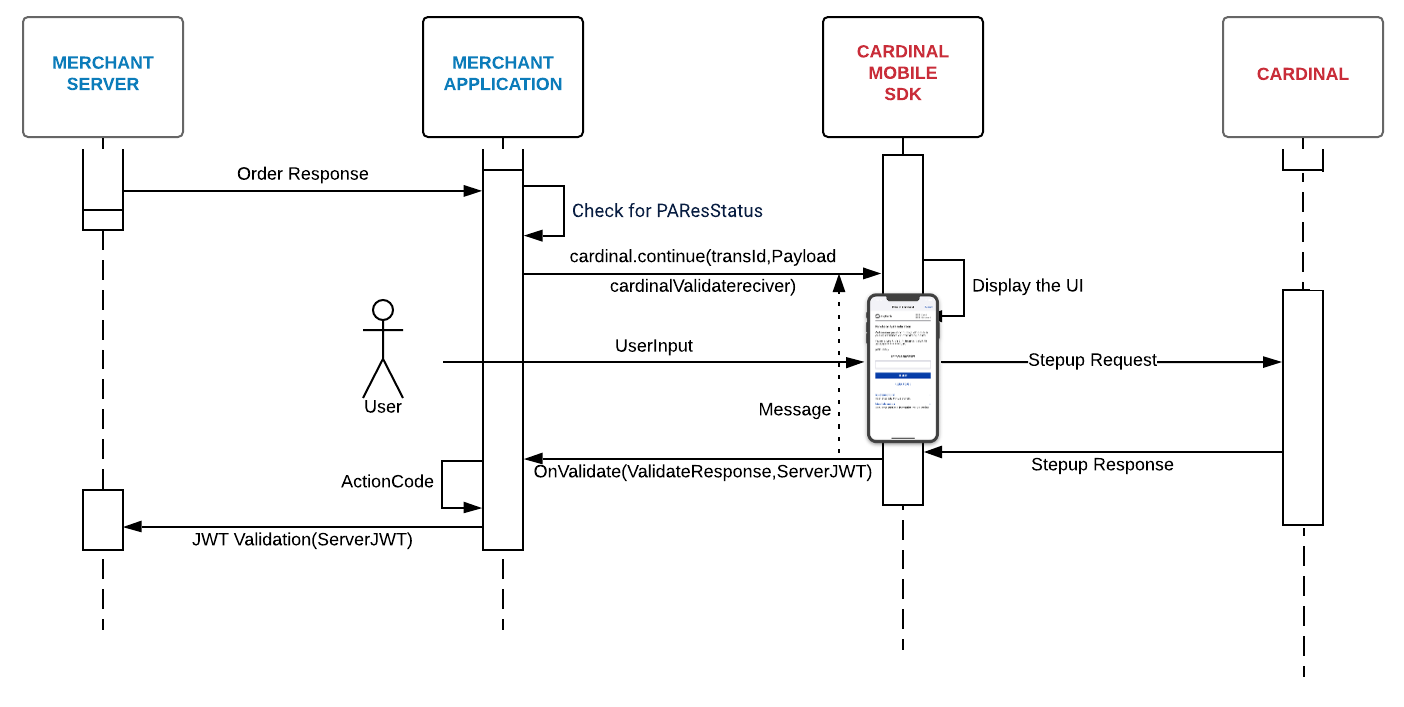
After the completion of the cmpi_lookup request, check the CMPI_Lookup_Response for the following fields :
- ThreeDSVersion = 2.X ( 2.0, 2.1, etc)
- Enrolled = Y
- PAResStatus = C
Upon validating the above fields, you will call cardinal.cca_continue to hand control to SDK for performing the challenge between the user and the issuing bank. Use the code snippet below for completing the cardinal.continue().
cardinal.cca_continue is updated to not passing the hardcoded directoryServerID anymore
cardinal.cca_continue("[TRANSACTION ID ]", "[PAYLOAD]", this, new CardinalValidateReceiver() {
});
/**
* Cca continue.
*
* @param transactionId the transaction id
* @param payload the payload
* @param currentActivity the current activity
* @throws InvalidInputException the invalid input exception
* @throws JSONException the json exception
* @throws UnsupportedEncodingException the unsupported encoding exception
*/
try {
cardinal.cca_continue("[TRANSACTION ID ]", "[PAYLOAD]", this, new CardinalValidateReceiver() {
/**
* This method is triggered when the transaction has been terminated. This is how SDK hands back
* control to the merchant's application. This method will
* include data on how the transaction attempt ended and
* you should have your logic for reviewing the results of
* the transaction and making decisions regarding next steps.
* JWT will be empty if validate was not successful.
*
* @param validateResponse
* @param serverJWT
*/
@Override
public void onValidated(Context currentContext, ValidateResponse validateResponse, String serverJWT) {
}
});
}
catch (Exception e) {
// Handle exception
}
/**
* Cca continue.
*
* @param transactionId the transaction id
* @param payload the payload
* @param currentActivity the current activity
* @throws InvalidInputException the invalid input exception
* @throws JSONException the json exception
* @throws UnsupportedEncodingException the unsupported encoding exception
*/
try {
cardinal.cca_continue("[TRANSACTION ID ]", "[PAYLOAD]", this, object: CardinalValidateReceiver {
/**
* This method is triggered when the transaction has been terminated.This is how SDK hands back
* control to the merchant's application. This method will
* include data on how the transaction attempt ended and
* you should have your logic for reviewing the results of
* the transaction and making decisions regarding next steps.
* JWT will be empty if validate was not successful.
*
* @param validateResponse
* @param serverJWT
*/
override fun onValidated(currentContext: Context?, validateResponse: ValidateResponse, serverJWT: String?) {
}
});
}
catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle exception
}
onValidated() is triggered when the transaction has been terminated. This is how the Cardinal Mobile SDK hands back control to the merchant's application. This event will include data on how the transaction attempt ended and should be where you review the results of the transaction and make decisions regarding the next steps. The field ActionCode should be used to determine the overall state of the transaction. On the first pass, we recommend that on an ActionCode of 'SUCCESS' or 'NOACTION' you send the response JWT to your backend for verification. There is more information on verifying JWT's in the next section.
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1602882423891&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=644&height=250)
@Override
public void onValidated(Context currentContext, ValidateResponse validateResponse, String serverJWT) {
switch (validateResponse.getActionCode()){
case SUCCESS:
// Handle successful transaction, send JWT to backend to verify
break;
case NOACTION:
// Handle no actionable outcome
break;
case FAILURE:
// Handle failed transaction attempt
break;
case CANCEL:
// Handle cancel transaction
break;
case ERROR:
// Handle service level error
break;
case TIMEOUT:
// Handle timeout
break;
}
}
override fun onValidated(currentContext: Context?, validateResponse: ValidateResponse, serverJWT: String?) {
when (validateResponse.getActionCode()!!) {
CardinalActionCode.SUCCESS -> {
// Handle successful transaction, send JWT to backend to verify
}
CardinalActionCode.NOACTION -> {
// Handle no actionable outcome
}
CardinalActionCode.FAILURE -> {
// Handle failed transaction attempt
}
CardinalActionCode.CANCEL -> {
// Handle cancel transaction
}
CardinalActionCode.ERROR -> {
// Handle service level error
}
CardinalActionCode.TIMEOUT -> {
// Handle timeout
}
}
}
Step 6 - JWT Validation
Once the response JWT arrives in the onValidated, you will need to send the response JWT to your backend for verification and consumption. We recommend that any values sent to 3rd parties are sourced from the response JWT after it has been properly validated.
Security Warning
For security reasons, all JWT validation must be done on the server side.
Looking for more information?
| Claim | Description |
|---|---|
| aud | Merchant jti Id - This is the 'jti' field from your request JWT echoed back. This field allows you to match up your request JWT with Cardinals response JWT. |
| jti | JWT Id - A unique identifier for this response JWT. This value is generated by Cardinal. |
| iat | Issued At Time - This is a timestamp of when the JWT was created. |
| iss | Issuer - The request JWT's iss field echoed back. |
| ConsumerSessionId | The unique session Id for the current user. |
| Payload | The response object for your request. This field will contain any actual state information on the transaction. This is the decoded data object that is passed into the payments.validated event as the first argument. |
JWT Payload Example
Below is an example of the JSON content of a basic response JWT Payload where we are passing an object within the Payload claim:
{
"iss": "56560a358b946e0c8452365ds",
"iat": 1471014492,
"exp": 1471021692,
"jti": "8af34811-f97d-495a-ad19-ec2f68004f28",
"ConsumerSessionId": "0e1ae450-df2b-4872-94f7-f129a2ddab18",
"Payload": {
"Validated": true,
"Payment": {
"Type": "CCA",
"ExtendedData": {
"CAVV": "AAABAWFlmQAAAABjRWWZEEFgFz+=",
"ECIFlag": "05",
"PAResStatus": "Y",
"SignatureVerification": "Y",
"XID": "MHEyQjFRQkttemdpaFlRdHowWTA=",
"Enrolled": "Y"
}
},
"ActionCode": "SUCCESS",
"ErrorNumber": 0,
"ErrorDescription": "Success"
}
}
Below is an example of the JSON content of a basic response JWT Payload where we are passing a string within the Payload claim. This would occur when the request JWT included a ObjectifyPayload flag set to false:
}
"iss": "56560a358b946e0c8452365ds",
"iat": 1471015342,
"exp": 1471022542,
"jti": "55ebfa2a-665f-4d6b-81ea-37d1d4d12d9e",
"ConsumerSessionId": "fb3a97a3-0344-4d3d-93ea-6482d866ec97",
"Payload": "{\"Validated\":true,\"Payment\":{\"Type\":\"CCA\",\"ExtendedData\":{\"CAVV\":\"AAABAWFlmQAAAABjRWWZEEFgFz+\\u003d\",\"ECIFlag\":\"05\",\"PAResStatus\":\"Y\",\"SignatureVerification\":\"Y\",\"XID\":\"MFpjUVpwb0FXcHdwMWJBdldwNDA\\u003d\",\"Enrolled\":\"Y\"}},\"ActionCode\":\"SUCCESS\",\"ErrorNumber\":0,\"ErrorDescription\":\"Success\"}"
}
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1602880595849&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=250&height=1261)
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1600304728430&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=1016&height=250)